Bond energy
- The same quantity of energy is involved when a particular bond is being broken or formed.
- The atoms in small inorganic molecules like water and carbon dioxide are joined by strong bonds, meaning that they require a lot of energy to break and release a lot when they form.
- Organic molecules like glucose contain many more bonds; these are weaker by comparison.
- They release less energy when they form and require less energy to be broken.
Equation
→ Representation
An → represents light in this equation
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆+6O₂
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
- Autotrophs such as plants can synthesise complex organic molecules such as carohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and vitamins from simple inorganic molecules like CO₂ and energy sources.
- Organisms that can photosynthesise are described as photoautotrophs
Chemoautotrophs
- Nitrifying bacteria → get energy from reactions such as oxidising nitrite to nitrate
- Bacteria living in darkness by thermal ocean vents
Heterotrophs
- Cannot make their own complex organic molecules from inorganic small molecules like CO₂ and H₂O but feed on and digest complex organic molecules into simpler soluble ones.
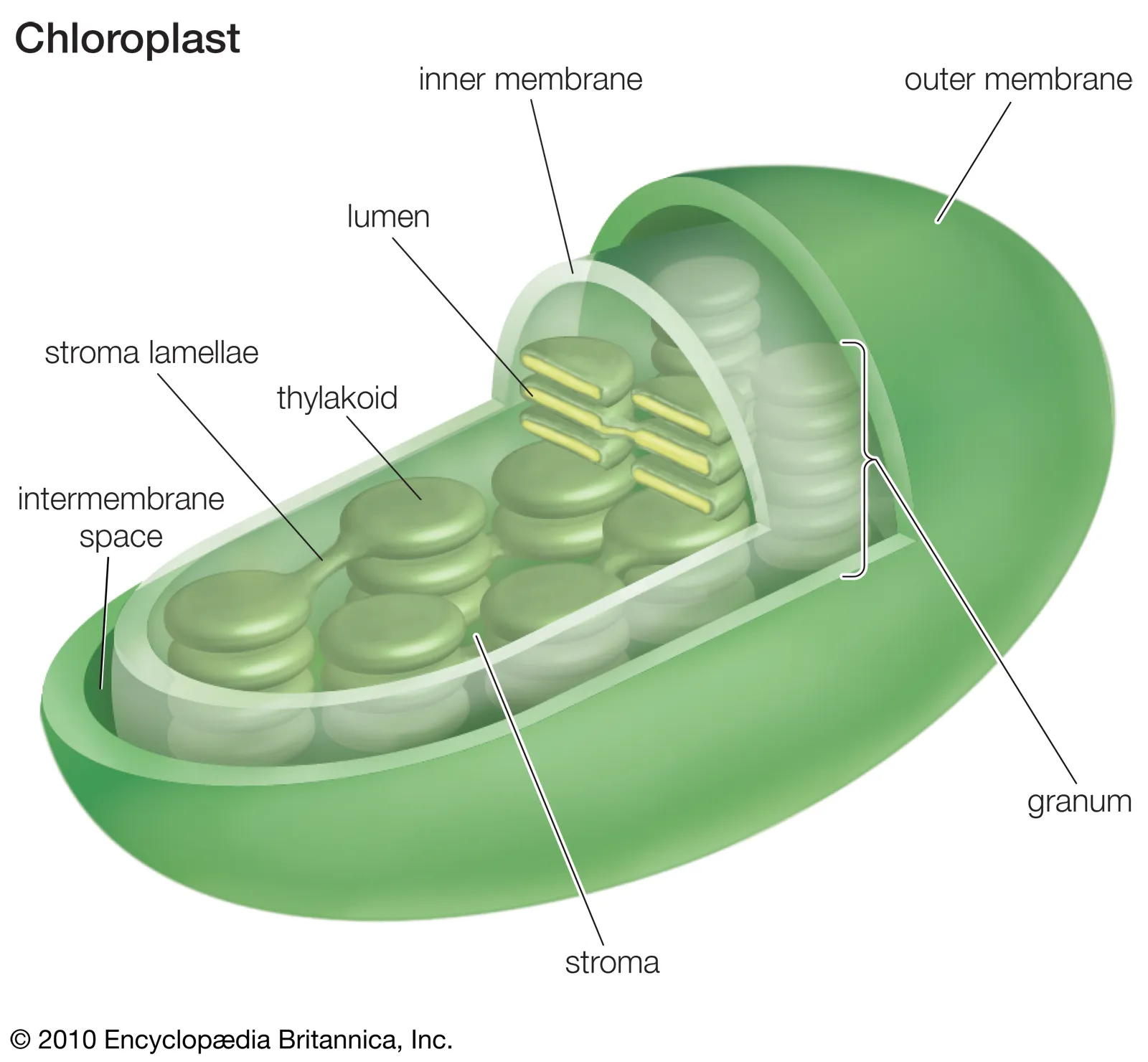
Chloroplasts
- 2-10 µm in length
- Usually disk shaped (sometimes varying)
- Surrounded by an envelope or double membrane
- Outer membrane is permeable to many small ions
- The inner membrane is less permeable and has embedded in it folded into llamellae (thin plates) which are stacked vertically. Each stack is called a granum.
- Between grana are integranal llamellae
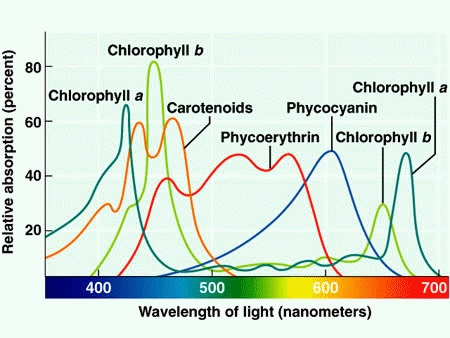
Photosynthetic Pigments
-
Absorb certain wavelengths of light
-
Funnel-shaped structures called photostems push light to a point
-
Proteins embedded in grana hold photostems in place
-
The fluid-filled stroma contains enzymes needed to catalyse reactions of the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis
-
Many grana, consisting of stacks of 100 thylakoid membranes provides a large surface area for the photosynthetic protein.
-
Grana surrounded by stroma so products of the light-dependent reaction (needed for light-independent reaction) can readily pass into stroma.
-
LIR - light independent reaction
-
LDR - light dependent reaction
-
Chloroplasts can make some of their proteins they need for photosynthesis using genetic instructions in chloroplast DNA, and the chloroplast ribosomes assemble the proteins.
-
Leaves contain a variety of pigments
-
Each absorbs a different range of light wavelengths
-
Maximises the amount of sunlight that can be absorbed